Authors: Nils Peterson, Matthew Sperzel, and Daniel Shats of the Institute for the Study of War
Editors: Dan Blumenthal and Frederick W. Kagan of the American Enterprise Institute
Data Cutoff: March 22 at 12pm ET
The
China–Taiwan Weekly Update focuses on the Chinese Communist Party’s
paths to controlling Taiwan and cross–Taiwan Strait developments.
Key Takeaways
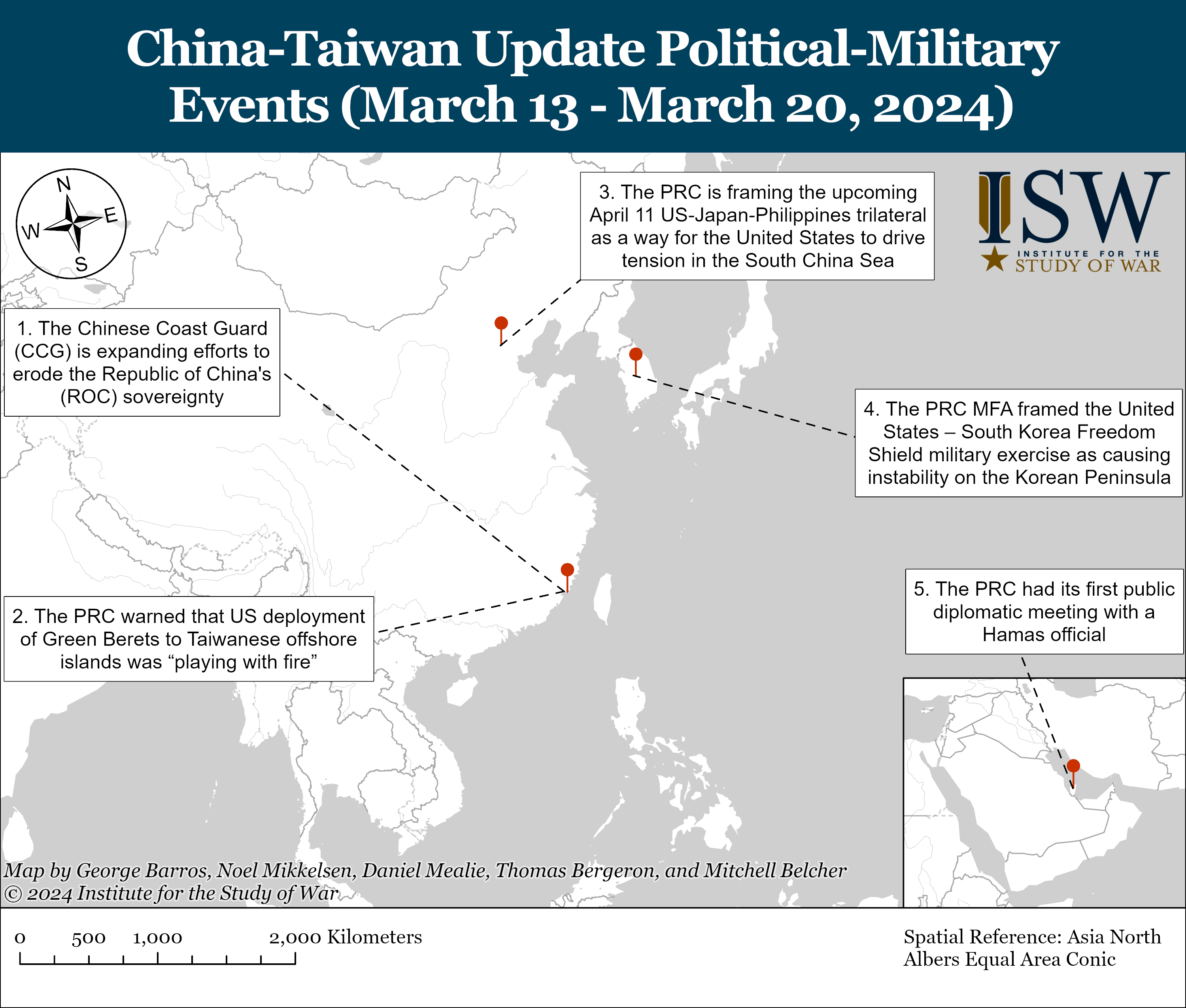
- The Chinese Coast Guard (CCG) is expanding efforts to erode the Republic of China's (ROC) sovereignty around Kinmen Island.
- The PRC Ministry of Defense (MOD) warned the United States was “playing with fire” in stationing Green Berets on the Kinmen and Penghu islands.
- The PRC is framing the upcoming April 11 US-Japan-Philippines trilateral as a way for the United States to drive tension in the South China Sea.
- The PRC MFA framed the United States–South Korea Freedom Shield military exercise as causing instability on the Korean Peninsula.
- The PRC had its first public diplomatic meeting with a Hamas official and its first diplomatic visits to Israel and Palestine since Hamas’ attack on Israel on October 7.
Cross-Strait Relations
Taiwan
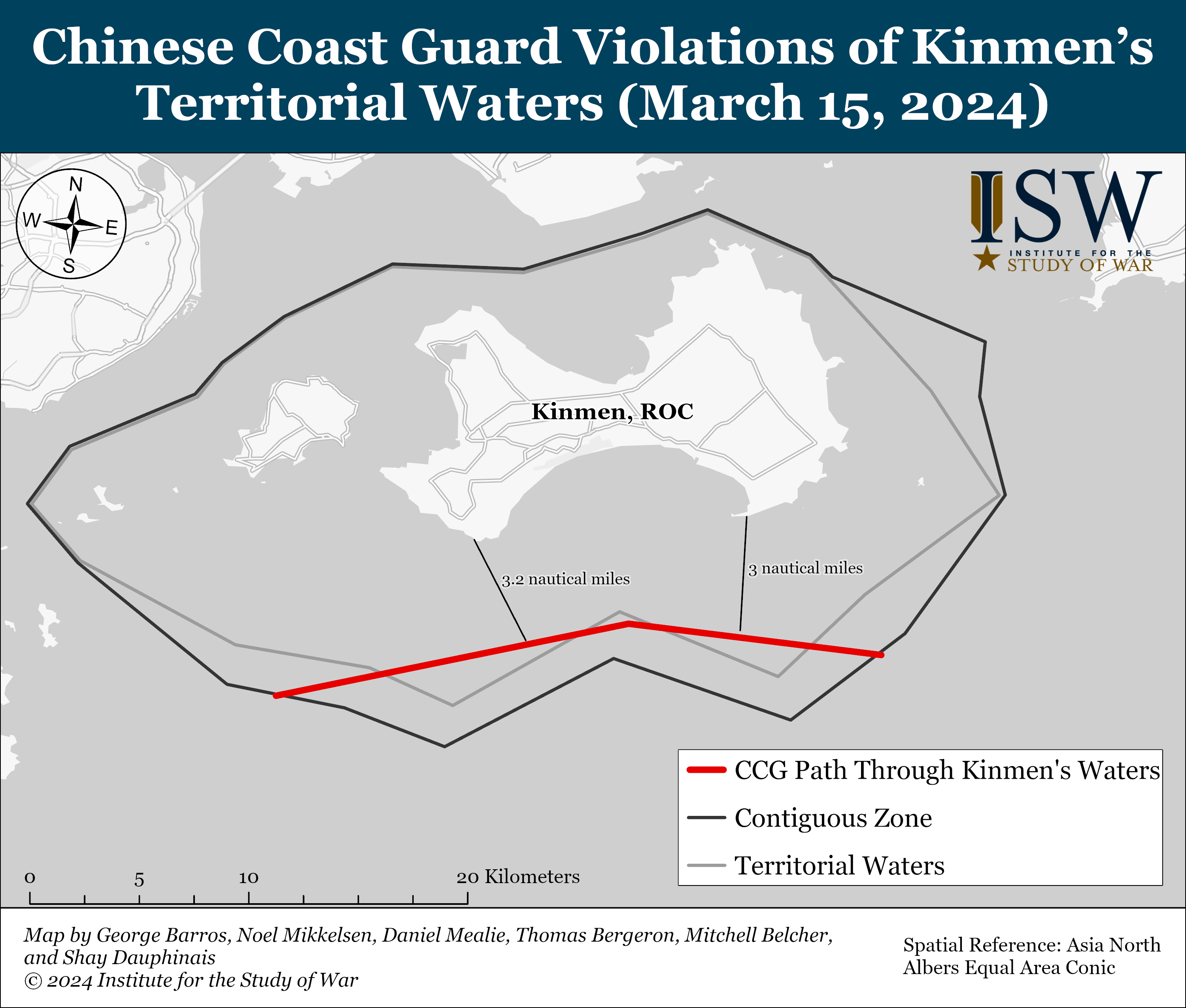
The Chinese Coast Guard (CCG) expanded its efforts to erode the Republic of China's (ROC) sovereignty around Kinmen Island.
Four CCG ships operated in Taiwan’s territorial waters around Kinmen
Island for two consecutive days for the first time on March 15 and 16.[1] One of the ships was a converted naval corvette that conducted the passage with its gun covers removed.[2] The CCG framed its operations as legitimate law enforcement to safeguard Chinese fishermen, including those from Taiwan.[3]
The CCG’s removal of its gun covers during its passage through Taiwan’s
waters illustrates its offensive posturing, indicating its actions are
intended to intimidate the Taiwanese Coast Guard rather than uphold a
safe maritime environment. CCG ships have previously used this tactic to
intimidate rival law enforcement in contested waters, including the
Philippines Coast Guard around Second Thomas Shoal in the South China
Sea.[4]
Kinmen
is a Taiwan-controlled island with a large military garrison roughly 3
kilometers from the coast of the PRC. The Taiwan Coast Guard
Administration (CGA) enforces maritime laws around Kinmen and its lesser
islands. The CCP does not accept Taiwan’s sovereignty over the waters
around the island, however.[5]
The
latest violations are part of a trend of CCG incursions following an
incident on February 14 in which a PRC fishing boat in Taiwan’s
prohibited waters near Kinmen capsized while fleeing from a legal
Taiwanese Coast Guard pursuit. The capsizing resulted in the deaths of
two of the four fishermen onboard. The CCG pledged on February 18 to
strengthen law enforcement activities around Kinmen. The CCG has
maintained a persistent presence around Kinmen and repeatedly violated
Taiwan’s maritime boundaries since then. The CCG boarded a Taiwanese
sightseeing ship on February 19, marking the first time a CCG ship
conducted inspections in Taiwanese waters.[6]
Five CCG marine surveillance ships entered Taiwan’s contiguous zone
around Kinmen on February 26, including one that crossed into
territorial waters.[7]
The total number of CCG ships around Kinmen reached 11 on February 27,
including two that entered Taiwan’s contiguous zone. Normalizing
operations around Taiwan’s waters sets conditions for the PRC to apply
further pressure on Taiwan in the future.
The rapid
normalization of CCG operations in Kinmen’s waters in response to the
incident suggests the PRC had pre-formulated reactions to this type of
contingency. The PRC exploited the capsizing incident as a pretense to
initiate a concerted coercion campaign that serves to incrementally
challenge and erode the ROC’s sovereignty in its adjacent waters.
The
PRC has shown that it is unwilling to return to the status quo before
the Kinmen incident. The CCG and CGA cooperated on a joint search and
rescue effort after a PRC fishing vessel capsized in PRC-controlled
waters around Kinmen on March 14.[8]
Both coast guards conducted search operations within their respective
jurisdictions. CGA Director Chou Mei-wu framed the cooperation as a
means to ease tensions with the PRC after the initial capsizing incident
in February.[9]
The CCG’s successive border violations on March 15 and 16 demonstrate
the PRC’s rejection of opportunities to de-escalate tensions as it
continues to erode ROC sovereignty around its outer islands.
The
Kuomintang (KMT) and Taiwan People’s Party (TPP) are pursuing political
reforms that threaten to undermine the Democratic Progressive Party’s
(DPP) governance by expanding legislative oversight of the executive
branch. The reforms aim to strengthen the Legislative Yuan’s
(LY) investigation rights by granting it more power to conduct inquiries
and call on officials to testify before the LY, establish penalties for
perceived non-compliance or dishonesty in responses, and empower the LY
to confirm political appointments.[10]
The TPP and KMT have consistently stated that establishing a
legislative investigative task force to strengthen oversight of the
executive branch is at the top of their agenda.[11]
KMT caucus Secretary-General Lin Tzu-ming earlier referred to the
proposed mechanism as a “great weapon” that the LY must use to supervise
the government.[12]
Collaboration between the KMT and the TPP on the proposals suggests
that the reforms will pass with a majority in the LY, as the two
opposition parties outnumber the DPP in the LY. The opposition’s plan to
impose checks and balances on the DPP could significantly hamper the
government’s ability to pass policy by miring it in defensive actions
against accusations of overstepping authority or corruption.
The
reforms have passed the initial stage and are scheduled for review by
the LY’s Judiciary and Organic Laws and Statutes Committee. DPP Caucus
Whip and LY Judicial Committee member Ker Chien-ming argued that the
reforms are unconstitutional. Ker threatened a procedural objection that
could delay the committee’s review process if the KMT did not arrange a
public hearing to scrutinize the bill.[13]
KMT Caucus Whip and LY Judicial Committee member Fu Kun-chi accused the
DPP of obstruction and stated that “only checks and balances will
prevent the DPP from falling into corruption.”[14]
The
PRC Ministry of Defense (MOD) warned the United States was “playing
with fire” in stationing Green Berets on the Kinmen and Penghu islands. US-based
special operations-focused online publication SOFREP first reported on
March 8 that US Army Special Forces (Green Berets) would be permanently
stationed at the Taiwanese Army’s amphibious command centers on the
outlying islands of Kinmen and Penghu.[15]
ROC Defense Minister Chiu Kuo-cheng responded to media inquiries about
the permanent presence of US troops in Taiwan on March 14 without
confirming the details of the SOFREP report. Chiu stated that
interactions with friendly countries fall within the scope of exchange
and cooperation, and help Taiwan’s armed forces recognize blind spots
and shortcomings in military preparedness.[16]
US service members have trained Taiwanese military personnel for
decades in an arrangement that Taiwan President Tsai Ing-wen first
acknowledged in 2021.[17]
Commander of the US Indo-Pacific Command John Aquilino said on March 20
that reports of US troops “permanently stationed” on Kinmen were
inaccurate, however.[18]
PRC
MOD spokesperson Zhang Xiaogang responded to the ROC claim on March 15
by stressing that the “Taiwan issue” is the first “insurmountable red
line” in US-PRC relations. Zhang said that the US troop deployment and
arms sales to Taiwan aimed to “weaken, hollow out, and distort” the
one-China principle and warned that “those who connive at and support
‘Taiwan independence’ separatist forces will get burned for playing with
fire and taste the bitter fruit of their own doing.” He said the PRC
military will “resolutely smash ‘Taiwan independence’ separatist
activities and external interfering attempts.”[19]
PRC officials strongly objected to Taiwan Vice President-Elect Hsiao Bi-khim’s visits to the United States and Czechia. Hsiao,
Taiwan’s former envoy to the United States, began a low-profile
“personal trip” to Washington DC during the week of March 12. Media
reports said that US and Taiwanese officials tried to keep the trip a
secret to avoid angering the PRC, but cited unnamed sources who said
Hsiao would meet with unspecified US officials to discuss her incoming
administration’s agenda.[20]
Spokesperson for the PRC embassy in the United States Liu Penghu called
Hsiao a “diehard Taiwan independence separatist” and expressed
Beijing’s firm opposition to her trip.[21]
Liu and MFA spokesperson Wang Wenbin both stressed the PRC “firmly
opposes” any official interaction between the United States and Taiwan.[22] Hsiao also visited Czechia on March 19 and met with Czech Senate President Miloš Vystrčil at a think tank event.[23] MFA spokesperson Lin Jian expressed opposition and warned Czechia to end its “bad behavior” of holding exchanges with Taiwan.[24]
China
The
PRC signaled strong opposition to a US bill that would ban TikTok in
the United States if TikTok’s PRC parent company does not sell its
stake. TikTok is owned by the PRC technology firm Bytedance.
PRC Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) spokesperson Wang Wenbin accused
the United States of overstretching the concept of “national security”
to hinder foreign competition, said the attempt to force the sale of
TikTok was based on “sheer robbers’ logic,” and warned that the US moves
would eventually backfire. Wang claimed the US government has never
found evidence that TikTok poses a national security threat.[25]
Wang also claimed the PRC’s bans on Facebook, Instagram, and other
Western social media were “completely incomparable” to the US approach
to TikTok because the PRC allegedly welcomes all foreign products and
platforms “as long as they observe Chinese laws,” while the US
government was discriminating against a specific company.[26]
TikTok
has claimed it never shares US user data with the PRC, but the US
government recommended that government employees avoid the app over
concerns that it may allow PRC access to user data.[27]
Former head of engineering for TikTok in the United States Yintao Yu
claimed in 2023 that CCP officials could access US user data from the
app.[28]
TikTok’s parent Bytedance is a private company but has an internal CCP
committee to regulate its “political direction,” like most large PRC
firms.[29]
The US Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI)
additionally stated that TikTok accounts run by a “PRC propaganda arm”
targeted US Congressional candidates during the 2022 midterm elections.[30]
Northeast Asia
Japan
The
PRC MOD framed the growth of Japan’s defense budget increase as
unjustified and militaristic rather than a response to regional security
issues, including PLA military coercion targeting Japan. The
Japanese Cabinet approved a USD 55.9 billion defense budget for Fiscal
Year 2024 in December 2023. The budget stipulates annual increases until
it reaches USD 62.5 billion for Fiscal Year 2027.[31]
The PRC MOD claimed on March 15 that this increase makes “the
international community question whether Japan… adheres to the path of
peaceful development.”[32]
The Japanese defense budget increase comes in response to PRC
aggression around the Japanese home islands. Japan’s Joint Staff noted
in January 2024 that it scrambled fighters 555 times in the last nine
months of 2023.[33]
98 percent of the scrambles responded to Chinese and Russian aircraft,
and more than 50 percent occurred near Japan’s southwest airspace, which
encompasses the Miyako Strait.[34]
North Korea
Russian
Deputy Foreign Minister Andrei Rudenko met with Chinese Special
Representative on Korean Peninsula Affairs Liu Xiaoming in Moscow on
March 19 to discuss the situation on the Korean Peninsula.[35]
Rudenko and Liu accused the United States and its allies of threatening
the military situation in northeastern Asia and warned the United
States against the proliferation of Cold War-style “bloc thinking.”[36]
The PRC MFA issued similar comments in framing the United States–South
Korea Freedom Shield military exercise as causing instability on the
Korean Peninsula.
Southeast Asia
Philippines
The
PRC is framing the United States as a destabilizing force in the South
China Sea ahead of the April 11 US-Japan-Philippines trilateral summit.[37] PRC
MFA Spokesman Wang Wenbin remarked on March 14 to a question about the
summit that the “US has traveled halfway around the world to China’s
doorsteps to form exclusive circles, flex muscles and make
provocations.”[38]
United States Secretary of State Antony Blinken reiterated an
“ironclad” commitment to the US-Philippine alliance on March 19 in the
ongoing aftermath of PRC revisionism in the SCS.[39]
PRC MFA Spokesman Lin Jian responded on March 19 that the United States
is “not a party” to South China Sea issues and therefore has no right
to “intervene” in Sino-Philippine disputes.[40]
The MFA’s rhetoric is consistent with previous PRC messaging about the
US role in the region. The PRC MOD framed the United States as “creating
bloc confrontations that escalate regional tension” after the June 2023
US-Japan-Philippines trilateral summit.[41]
The
messaging from the PRC MFA aims to deflect blame from the PRC for
heightened tensions in the South China Sea, namely over the Scarborough
Shoal and Second Thomas Shoal. Scarborough Shoal is a contested atoll
that the PRC and the Philippines claim and that has been under de facto
PRC control since 2012.[42]
The Chinese Coast Guard (CCG) erected a floating barrier and
intercepted Philippine Coast Guard vessels in February to deny the
Philippines access to the shoal.[43]
The CCG has also disrupted Philippine Coast Guard missions to ensure
the security of Filipino fishermen near the shoal. The Second Thomas
Shoal is a submerged reef in the Spratly Islands in the South China Sea
which the Philippines and the PRC both claim. The Philippines controls
the shoal with troops based on the grounded warship BRP Sierra Madre.
A CCG vessel attempted to block and collided with a Philippine Coast
Guard (PCG) vessel escorting a supply mission to Second Thomas Shoal on
March 5, causing minor damage to the Philippine ship.[44]
Two CCG ships also fired water cannons at a separate Philippine supply
ship, injuring four Philippine personnel, and later collided with it.[45]
The
CCG actions In the South China Sea support PRC claims of sovereignty
over nearly the entirety of the South China Sea, including the Spratly
Islands, through the “nine dash line” maritime boundary. The PRC rejects
a 2016 Permanent Court of Arbitration ruling that declared the nine
dash line claims are unlawful.[46]
The PRC has constructed, seized, and attempted to seize many islands in
the South China Sea so it can build a military presence throughout the
critical waterway. The PRC has built military infrastructure on islands
that it has seized control of or artificially constructed to expand its
power projection capability, strengthen domain awareness, and increase
its control over critical Sea Lines of Communication (SLOCs) through the
South China Sea. Developing the capability to monitor or restrict ships
through the South China Sea would support a future PRC effort to
implement a blockade of Taiwan or block US and allied reinforcements
from reaching the Taiwan Strait in wartime.
Australia
PRC Foreign Minister Want Yi visited Australia and New Zealand between March 17 and 21. Wang’s
meeting with New Zealand Foreign Affairs Minister Winston Peters
addressed implementing the China-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement, as
well as disagreements over New Zealand’s potential ascension into AUKUS.[47]
The PRC MFA framed Wang’s separate meetings with Australian Prime
Minister Anthony Albanese and Australian Foreign Affairs Minister Penny
Wong as seeking common ground and opportunities for Sino-Australian
collaboration.[48] Wang’s visit to Australia also included meetings with the Australian business community and former Prime Minister Paul Keating.[49] Keating is a prominent critic of AUKUS and a former board member of the CCP-run China Development Bank.[50] This is the first visit by a PRC foreign minister to Australia since 2017.[51]
Europe
Russia-Ukraine War
The
PRC advocated for direct dialogue between Russia and Ukraine without
committing to the Ukraine-proposed “global peace summit” in Switzerland.
PRC Ambassador to Switzerland Wang Shihting said in an interview on
March 18 that the PRC supports direct dialogue between Russia and
Ukraine as soon as possible. He also stated that the PRC is “examining
the possibility of taking part” in the Ukraine-proposed “global peace
summit." [52]
MFA spokesperson Lin Jian subsequently avoided directly answering
whether the PRC would participate in the summit or whether it would push
for Russia to participate.[53]
Wang
Shihting’s comments do not signal a change in PRC policy toward the war
in Ukraine. The PRC has consistently backed peace talks or negotiations
between Russia and Ukraine, in abstract terms, and portrayed itself as
an impartial and “stabilizing” force in pushing for a political
settlement to end the war. It has not committed to any specific peace
talk proposals, however. PRC Foreign Minister Wang Yi dismissed
Ukraine’s proposal for peace talks in Switzerland on February 17 during
the Munich Security Conference, stating that there were not “ripe
conditions” for peace talks, in comments that were omitted from PRC
readouts.[54]
Wang Yi told the National People’s Congress on March 7 that the PRC
supports holding “in due course” an international peace conference
recognized by both Russia and Ukraine.[55] Russia has said it will not participate in the summit even if invited.[56]
PRC Special Envoy for Eurasian Affairs Li Hui reiterated PRC support
for a “timely convening of an international peace conference” but
acknowledged on March 22 that “there is a relatively big gap in [the
Russian and Ukrainian] understanding of peace talks.” Li’s
acknowledgement of differences in the two sides’ understanding of peace
talks was absent from the PRC readout of his remarks.[57]
The
PRC rhetorically aligns with Russian framing in criticizing NATO,
portraying the Western security order and arms sales to Ukraine as
fueling the war, opposing sanctions on Russia, and calling for respect
for Russia’s “legitimate security concerns.”[58] The PRC has not shown any willingness to pressure Russia to end the war.
Middle East
Israel-Hamas War
The
PRC had its first public diplomatic meeting with a Hamas official and
its first diplomatic visits to Israel and the West Bank since Hamas’
attack on Israel on October 7. PRC MFA envoy Wang Kejian met
with the head of Hamas’ political bureau Ismail Haniyeh in Doha, Qatar
on March 17. This was the first meeting between PRC and Hamas officials
that the PRC has publicly acknowledged since the war in Gaza began in
October 2023. Hamas claimed that Wang called Hamas “part of the
Palestinian national fabric” and said the PRC is “keen on relations with
it.”[59] The PRC readout simply said Wang and Haniyeh “exchanged views on the Gaza conflict.”[60]
The PRC has not publicly criticized Hamas since the war began. MFA
Spokesperson Lin Jian said on March 19 that the PRC supports the
Palestinian Authority in governing all Palestinian territories and
called for “internal reconciliation” among all political factions in
Palestine, however.[61]
Wang, who is a former ambassador to Lebanon, has been in the Middle East since at least March 10 discussing the Gaza war with officials in Egypt, Israel, the West Bank, and Qatar.[62] He led the PRC’s first diplomatic trip to Israel and Palestine since the war began, meeting with Palestinian Authority Foreign Minister Riyad al Maliki in the West Bank on March 13 and Israeli foreign ministry officials Hagai Shagrir and Rachel Feinmesser in Israel on March 14. The PRC readouts for the meetings in Israel and the West Bank said Wang reiterated the PRC support for a ceasefire in Gaza, humanitarian aid, and the promotion of a two-state solution, though these policy positions were absent from the readout of the Hamas meeting.[63] This has been the PRC’s consistent stance on the conflict, which broadly aligns with the view of Arab states and allows the PRC to portray itself as a responsible great power that is pushing for peace. PRC Foreign Minister Wang Yi endorsed Palestine becoming a full member of the UN on March 7.[64]
[1] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gofLzuNU8T4
https://www.cna dot com.tw/news/acn/202403160065.aspx
https://www.ccg dot gov.cn//2024/hjyw_0315/2433.html
[2] https://www.chinatimes dot com/realtimenews/20240319000055-260407
[3] https://www.ccg dot gov.cn//2024/hjyw_0315/2433.html
[4] https://www.navalnews.com/naval-news/2023/02/china-harasses-pcg-vessel-amid-increased-philippine-maritime-security-cooperation-with-japan-u-s/
[5] www.gwytb dot gov.cn/m/speech/2024-3/t20240313_12605908.htm
[6] https://www.cga dot gov.tw/GipOpen/wSite/ct?xItem=159716&ctNode=650&mp=999
[7] https://www.taiwannews dot com.tw/en/news/5104572
[8] https://www.cna dot com.tw/news/aipl/202403140082.aspx
[9] https://news.ltn dot com.tw/news/politics/breakingnews/4607695
[10] https://udn dot com/news/story/123475/7822131
[11] https://udn dot com/news/story/123475/7718848
https://www.chinatimes dot com/opinion/20240208002816-262101
[12] https://www.chinatimes dot com/realtimenews/20240206002157-260407?chdtv
[13] https://www.cna dot com.tw/news/aipl/202403170066.aspx
[14] https://www.chinatimes.com/cn/realtimenews/20240320002276-260407
[15] https://sofrep.com/news/us-army-special-forces-to-be-deployed-on-taiwanese-island-six-miles-from-mainland-china/
[16] https://www.cna dot com.tw/news/aipl/202403140047.aspx
[17] https://www.cnn.com/2021/10/27/asia/tsai-ingwen-taiwan-china-interview-intl-hnk/index.html
https://sofrep.com/news/us-army-special-forces-to-be-deployed-on-taiwanese-island-six-miles-from-mainland-china/
https://www.newsweek.com/american-special-forces-train-taiwan-soldiers-penghu-kinmen-china-coast-1868009
[18] https://www.taiwannews dot com.tw/en/news/5119823
https://focustaiwan dot tw/politics/202403210009
[19] http://www.mod dot gov dot cn/gfbw/qwfb/16294196.html
[20] https://www.wsj.com/world/asia/taiwans-incoming-vp-is-on-a-low-profile-visit-to-washington-ed59d07b?mod=china_news_article_pos2
[21] https://news.ltn dot com.tw/news/politics/breakingnews/4605896
[22] https://www.fmprc dot gov dot cn/fyrbt_673021/202403/t20240313_11260196.shtml
[23] https://focustaiwan dot tw/politics/202403190008
[24] https://www.mfa dot gov dot cn/web/wjdt_674879/fyrbt_674889/202403/t20240319_11262628.shtml
[25] https://www.fmprc dot gov dot cn/fyrbt_673021/202403/t20240313_11260196.shtml
https://www.fmprc dot gov dot cn/fyrbt_673021/202403/t20240314_11260824.shtml
[26] https://www.fmprc dot gov.cn/fyrbt_673021/jzhsl_673025/202403/t20240315_11261387.shtml
[27] https://www.chinatimes dot com/cn/realtimenews/20240320002276-260407 https://www.dni.gov/files/NCSC/documents/nittf/OPSEC_Advisory_TikTok_Concerns_and_Vulnerabilities.pdf
[28] https://apnews.com/article/tiktok-china-bytedance-user-data-d257d98125f69ac80f983e6067a84911
[29] https://www.reuters.com/technology/what-do-we-know-about-tiktoks-chinese-owner-bytedance-2024-03-15/
http://www.ce dot cn/xwzx/kj/201809/29/t20180929_30414651.shtml
[30] https://www.odni.gov/files/ODNI/documents/assessments/ATA-2024-Unclassified-Report.pdf
[31] https://news.usni.org/2023/12/22/japanese-cabinet-approves-largest-ever-defense-budget
https://apnews.com/article/japan-military-budget-us-china-missile-5e1e2c40890b3ca8ea682c2dc91f9553
[32] http://www.mod dot gov.cn/gfbw/xwfyr/jt/16294372.html
[33] https://www.mod.go.jp/js/pdf/2024/p20240123_02.pdf
[34] https://www.mod.go.jp/js/pdf/2024/p20240123_02.pdf
[35] https://t.me/MID_Russia/37120
[36] https://t.me/MID_Russia/37120
[37] https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2024/03/18/statement-from-press-secretary-karine-jean-pierre-on-the-upcoming-trilateral-leaders-summit-of-the-philippines-japan-and-the-united-states/
[38] https://www.mfa dot gov.cn/web/wjdt_674879/fyrbt_674889/202403/t20240314_11260824.shtml
[39] https://www.state.gov/secretary-blinkens-meeting-with-philippine-president-marcos-jr/
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-68594365
[40] https://www.mfa dot gov.cn/web/wjdt_674879/fyrbt_674889/202403/t20240319_11262628.shtml
[41] https://www.chinadaily dot com.cn/a/202306/29/WS649d8268a310bf8a75d6c625.html
[42] https://amti.csis.org/counter-co-scarborough-standoff/
[43] https://twitter.com/barnabychuck/status/1761549762673955263
[44] https://www.gmanetwork dot com/news/topstories/nation/899475/pcg-china-actions-led-to-collision-during-latest-ayungin-resupply-mission/story
[45] https://twitter.com/jaytaryela/status/1764902394381643825
https://www.gmanetwork dot com/news/topstories/nation/899501/4-hurt-after-china-vessels-water-cannoned-ph-resupply-boat-gov-t-task-force/story/?just_in
[46] https://news.usni.org/2016/07/12/document-overview-south-china-sea-tribunal-decision
[47] https://www.fmprc dot gov.cn/mfa_eng/zxxx_662805/202403/t20240319_11262568.html
https://www.dw.com/en/chinas-foreign-minister-begins-new-zealand-australia-tour/a-68610715
[48] https://www.mfa dot gov.cn/web/wjdt_674879/wjbxw_674885/202403/t20240320_11262956.shtml
https://www.mfa dot gov.cn/web/wjdt_674879/wjbxw_674885/202403/t20240320_11263395.shtml
[49] https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/chinese-foreign-minister-meet-former-australia-pm-keating-visit-2024-03-18/
[50] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P3m3U-CK8L4
https://www.theguardian.com/australia-news/2023/mar/15/paul-keating-labels-aukus-submarine-pact-worst-deal-in-all-history-in-attack-on-albanese-government
https://apnews.com/article/technology-business-australia-france-paul-keating-cbb8195ddc24ac603cf8c4ec43d843a3
[51] https://www.dw.com/en/chinas-foreign-minister-begins-new-zealand-australia-tour/a-68610715
[52] https://www.reuters.com/world/china-considers-taking-part-swiss-ukraine-peace-talks-ambassador-says-2024-03-18/
[53] https://www.mfa dot gov dot cn/web/wjdt_674879/fyrbt_674889/202403/t20240318_11262087.shtml
[54] https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2024-02-17/ukraine-seeks-to-meet-chinese-minister-to-discuss-peace-summit
[55] https://english.news dot cn/20240307/54b43e93d2e24cc0881f3db31f7edc22/c.html
[56] https://www.yahoo.com/news/russia-says-not-participate-switzerland-164718890.html
[57] https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/russia-ukraine-see-crisis-eventually-resolved-through-talks-chinas-special-envoy-2024-03-22/
https://www.mfa dot gov dot cn/web/wjdt_674879/sjxw_674887/202403/t20240322_11266021.shtml
[59] https://t.me/hamasps/19765
https://www.jpost dot com/breaking-news/article-792430
[60] https://www.mfa dot gov dot cn/wjdt_674879/sjxw_674887/202403/t20240319_11262449.shtml
[61] https://www.mfa dot gov dot cn/web/wjdt_674879/fyrbt_674889/202403/t20240319_11262628.shtml
[62] https://www.cnn.com/2024/03/19/china/chinese-envoy-hamas-meeting-israel-intl-hnk/index.html
[63]https://www.mfa dot gov dot cn/wjdt_674879/sjxw_674887/202403/t20240314_11260526.shtml
https://www.mfa dot gov dot cn/wjdt_674879/sjxw_674887/202403/t20240315_11261101.shtml
[64] https://www.fmprc dot gov dot cn/eng/zxxx_662805/202403/t20240308_11256419.html